Software
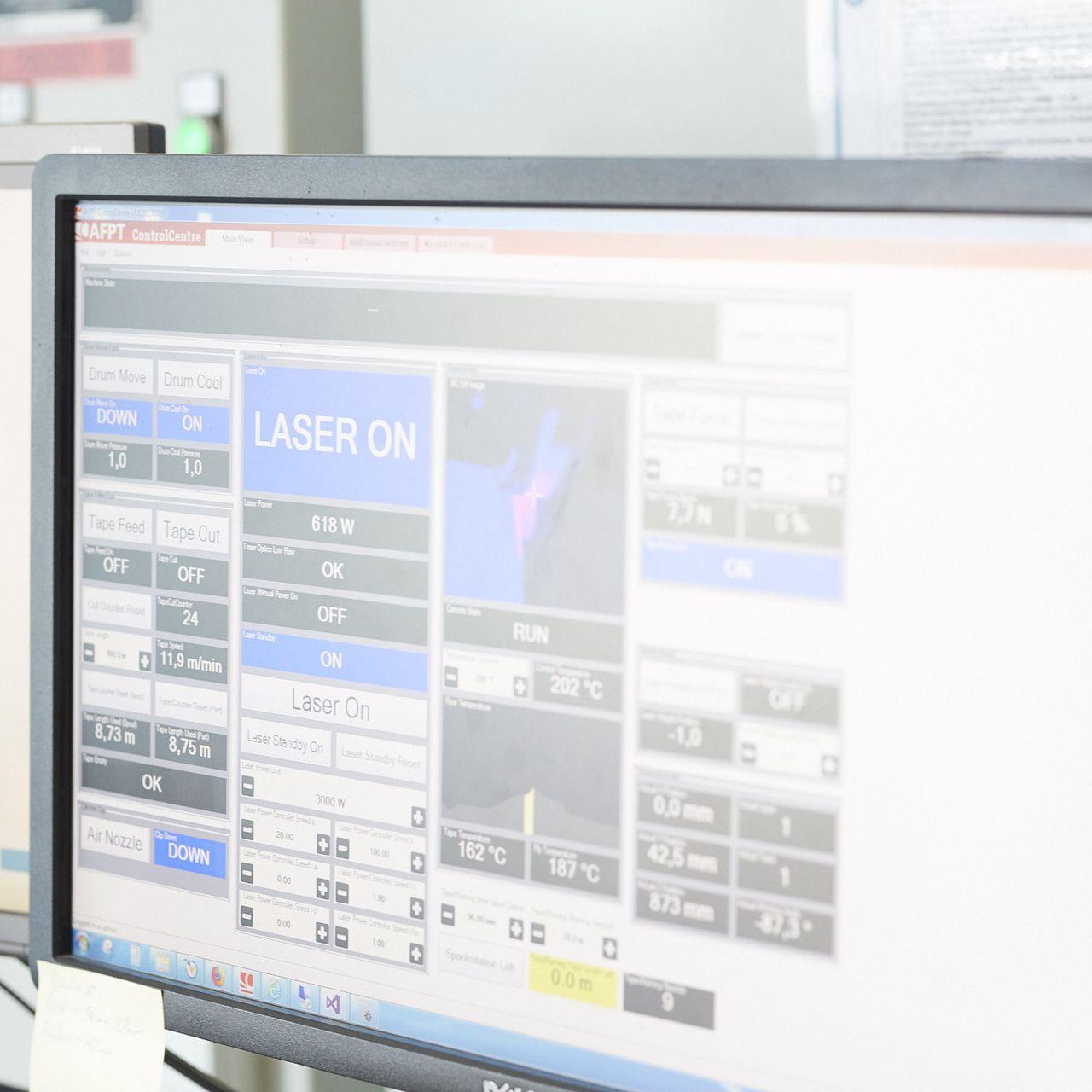

Control Center
For Human-Machine Interaction
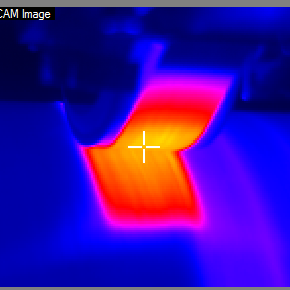
Closed-Loop Control
For the Ideal Consolidation
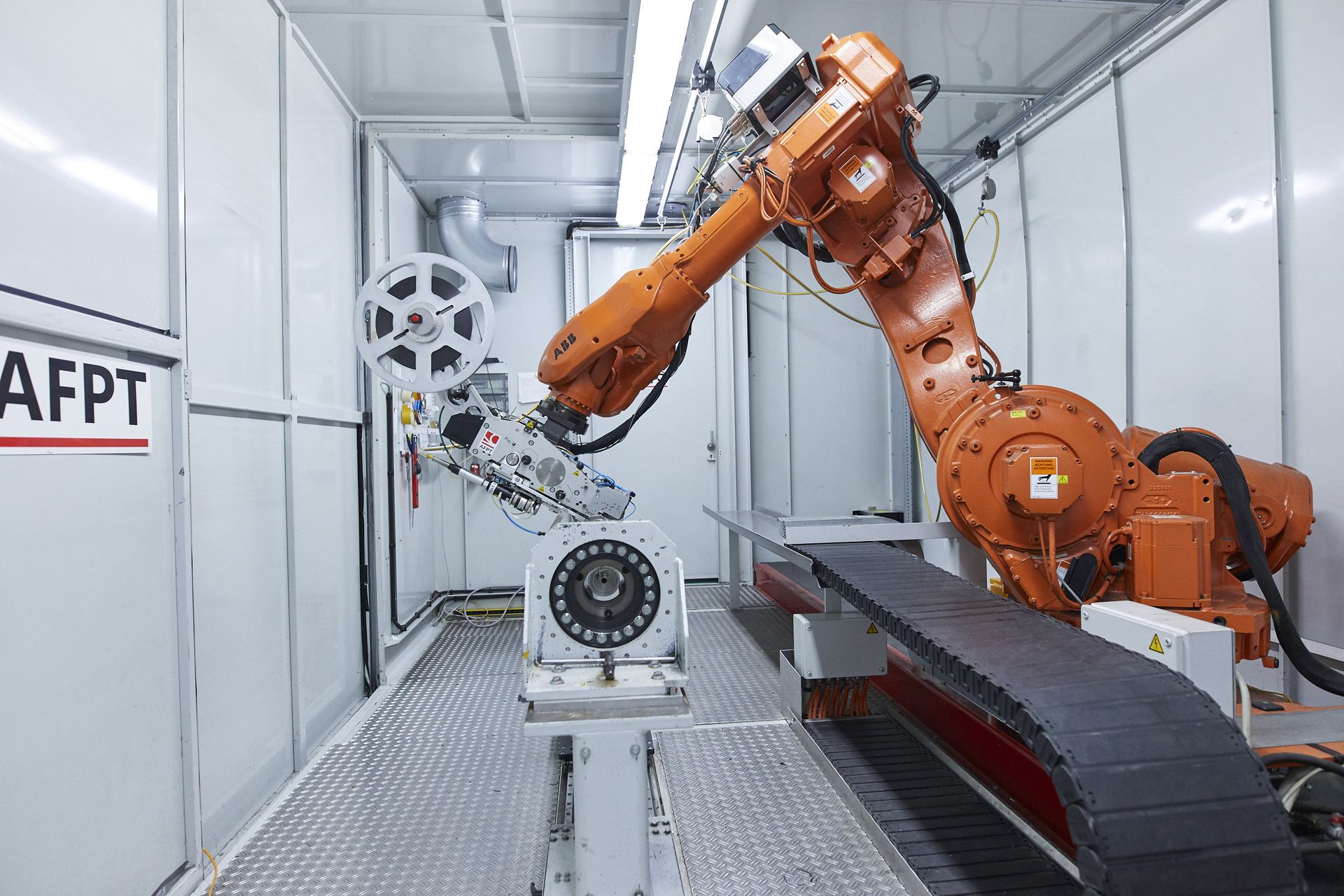

Post Processor
For Kinematic Control
Data Logger
For Process Quality Monitoring
Essential to operating a LATW/LATP process is the software to control the equipment, as well as the process. AFPT's equipment comes with a software package that contains up to four main components: a HMI, a closed-loop process control system, a post processor and a data logger.
AFPT's Control Center is the graphic user interface which allows an operator to adapt and monitor all relevant process parameters such as tape tension, consolidation pressure, tape speed, laser power, and process temperatures. The interface displays communication with the laser and kinematic system (laser power feedback and position (X, Y, Z) of placement head, as well as visualization of infrared camera image and temperature distribution to help monitor the process quality.
The post processor is adaptable to the most common robot, CNC, and gantry systems. These systems provide the movement and action control of AFPT's effector. Based on inputs for the desired part geometry, the post processor will define the path of movement and signals such as when the laser turns on or when the tape is to be cut.
The heart of AFPT's LATW/LATP process is it's robust closed-loop process control which uses an infrared camera to monitor the process and automatically adjusts laser power and angle to achieve the desired consolidation. By reading the temperature of the incoming tape, as well as the already laid substrate, it can be ensured that the nip-point (when the tape and substrate join) achieves the target temperature to fully melt the thermoplastic matrix.
The process in inherently digital, which allows the storage of all relevant measurements with high frequency in a SQL Database for offline or online quality control with warnings and error messages if temperature limits are not met. Aggregated data tables with quality numbers allow quick checks if the quality changes over time or with a new material batch. Ply-based reports for every part or part-based reports for a full production batch are example of what can be provided to the end user of the products produced.